Proxifier can resolve hostnames through a proxy server, which is a valuable feature when local name resolution does not work properly or causes problems. Generally, it is not recommended to use this feature in all other cases as it has some limitations in comparison to the normal method of resolution. For example, it is impossible to get a real IP address through a proxy, so Proxifier must assign a placeholder (fake) IP address, such as 127.8.*.*, that is valid only within the local computer. Also, Proxification Rules based on IP addresses will not work in this case.
To configure name resolution, choose in the menu or the corresponding icon on the toolbar. The Name Resolution dialog will appear.
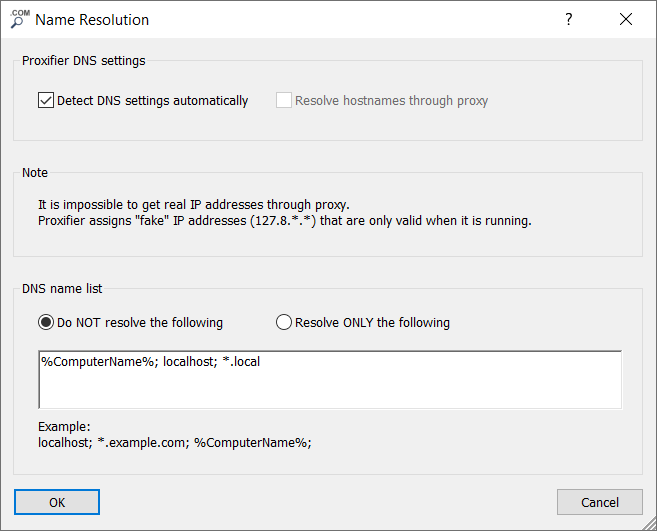
By default, the mode is enabled. In this case, Proxifier continuously monitors the network condition. If system DNS is unavailable, Proxifier automatically enables the option.
You can disable the automatic mode and enable/disable this option manually.
Proxifier outputs the following message when it changes the DNS mode automatically:
(Automatic DNS mode detection) Local DNS service is available/unavailable. Name Resolution through proxy is disabled/enabled.
The current DNS mode is also indicated at the bottom of the main window.
The contains specific names that should be processed according to the selected option:
You can use wildcards (masks) with “?” matching any symbol and “*” matching any substring.
The %ComputerName% constant is automatically replaced with the local computer name during the processing.
The %SimpleHostnames% constant defines all names that do not contain a domain/subdomain (i.e., there are no dot-separated parts). Usually, such hostnames are used with a local network, so it makes no sense to resolve them through a proxy.
Proxifier will output DNS requests if the or log mode is enabled at or at . This can be useful when investigating problems related to DNS.
The name resolution settings are stored in Proxifier profiles and can be saved/loaded similarly to other settings.